
- 0 comments0
- 2 views
 By Team Biliti Electric
By Team Biliti Electric
Are you an EV owner? Does your vehicle often run out of charge in the middle of your journey? Or are you sick of waiting hours to charge your vehicles at the charging stations? You need not worry further. This article gives you a whole bunch of information regarding DC Fast EV Charging. This will help you charge your vehicle faster compared to AC chargers. Now, you don't have to wait for tiring long hours, and your vehicle will be ready to go within much lesser time.
What is a DC fast charger?
The charging of EVs can be done with both AC and DC charging. EV works on DC power, whereas the electric grid delivers Alternating Current (AC). All EVs have an onboard charger that converts AC to DC before transferring the power to the vehicle’s battery. Whether you are charging your vehicle with a Level 1 or Level 2 charger, your Electric vehicle gets power in AC. Then it converts it into DC before reaching the vehicle’s battery. This process takes more time and increases the charging time of the automobile.
Direct current or DC fast charger for electrical vehicles is the fastest way to charge your electric car as it supplies DC power directly to the EV’s battery. It is essential for long-distance travel and the sustained adoption of EVs. If you are learning to understand how much it would cost for charging an EV, then do click on the linked blog post for more information.
Levels of DC fast charging
Level 1 charging
Have you ever used a household outlet to charge your gasoline car battery at the time of extreme cold? The same charging in the EV world is called level 1 charging. It is the slowest mode of charging your EV, and it takes more than 24 hours to charge it fully. Level 1 charger needs a 120-volts outlet for the plugin. The typical power output is between 1 and 1.7 kW, which adds 3 to 7 miles of range to your electric vehicle every hour. Plus, you can only charge one vehicle at a time, making it more time-consuming. Using Level 1 charging might be good in an emergency, but we don’t recommend using them regularly. Also, in other parts of the world outside North America, the Standard household supply is 230 volts, making it not feasible for Level 1 chargers.
Level 2 Charging
Level 2 chargers are one step above the level 1 charger and need around 208V to 240V outlets in the North American region, while 230 volts for single phase and 400 volts for three-phase connection in Europe. Level 2 chargers generally offer output between 3kW to 22kW but vary with different regions of the world, resulting in 10 to 75 miles of range for around one hour’sworth of charge. Level 2 chargers are plugged directly into the electrical panel or special outlet made exclusively for them. It is the most famous and commonly used method of charging EVs and can be easily found in garages, workplaces, and many public locations. The only downside of Level 2 chargers is that they deliver current in AC and are comparatively slower than level 3 ones.
Level 3 charging
The fastest method of charging currently available is the Level 3. It utilizes DC power to charge your EV’s battery, making it faster than the other two former types. Level 3 chargers generally offer 15kW to 350kW output and fully charge your EV in just 15-60 minutes. DC fast charger uses three-phase connections, which makes it blazing fast and the most lucrative method of charging. If you are always on the go and want a fast EV charging method, then level 3 DC charging is all you need.
Also Read:- Types of Electric Vehicle Charging Connectors
How does DC fast charging work?
The electric vehicle is in constant communication at the time of DC fast charging to regulate how much power is drawn. Several factors affect the rate at which your EV gets charged. However, the main factors include the charge acceptance rate of the vehicle, the rate of charge of the charging station, and the DC fast charging curve.
Rate of Charge of the station
DC fast charging station use kilowatts (kW) to measure their maximum output power, also called charging rate or rate of charge. These fast-charging stations usually range from 15kW to 350kW. The higher the output power (kW), the faster the charging rate. However, only DC chargers with high kW do not necessarily speed up the charging rate. It depends on other factors as well.
Electric Vehicle charge accepting rate
The maximum amount of power in kW an electric car can take as input is its charge acceptance rate. A vehicle’s built-in battery management system communicates this to the station when your EV is connected using a DC fast charging cable. Most of the old electric vehicles have very low charge-accepting rates. Still, with development in modern technology now, more EVs with charge-accepting rates are coming to market to improve their charging rate.
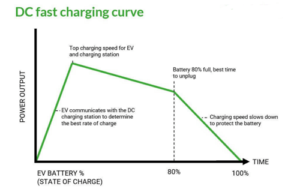
DC fast charging curve
Every EV model has its own charging curve, that determines the amount of power it can take over time as it charges.
Charging Types
We know that Level 3 DC chargers are the fastest charging method but are also of three types. In North American Countries such as the US and Canada, DC chargers are of three basic types: Combined Charging System (CCS), CHAdeMO, and Tesla Supercharger.
Combined Charging System (CCS)
The Combined charging system or CCS works on a universal standard for electric vehicles. As the name suggests, it combines one-phase, three-phase AC, and high-speed DC, making it very powerful and one of the fastest charging methods. This system is very easy to use and includes the inlet and connecter combination to control all the functions easily. The system is a standardized one and is used globally. Almost all automobile companies use the CCS standard in the US and other parts of North America. Automotive giants such as Ford, Fiat, Hyundai, Kia, Volvo, Rolls Royce, and many other reputed brands used CCS for EV charging.
CHAdeMO
A famous DC charging system developed by Tepco, Japan. It is the most famous and commonly used system in Japan. The most amazing thing about this system is that it establishes a seamless connection between the charger and the vehicle. Also, Unlike the CCS system, CHAdeMO connections never share a portion of the connection with the J1772 inlet.
The system is now spreading rapidly and has members from around the globe. To spread the system, CHAdeMO has opened its branch in Paris, France, to work with European members actively.
Tesla Supercharger
Tesla has developed superchargers that are only compatible with Tesla vehicles. A non-tesla automobile cannot be charged using Tesla Supercharger Station or an adaptor cable. To maintain its hegemony, Tesla has set up around 16,000 DC fast charging stations in the US and different parts of North America.
How does DC fast charging work?
The speed of DC charging depends on different factors, from the type of automobile to battery capacity. There is not a 100 percent accurate answer for this. However, an estimated answer is possible.
We have estimated data based on the power output of the charger and the average EV's kWh per 100 miles, which is 34.6; we can estimate the number of miles of range an electric car can receive from a DC fast charger in 60 minutes.
| 30 kW | 87 miles per hour |
| 5o kW | 145 miles per hour |
| 100 kW | 289 miles per hour |
| 120 kW | 347 miles per hour |
| 150 kW | 434 miles per hour |
| 180 kW | 520 miles per hour |
| 250 kW | 723 miles per hour |
| 350 kW | 1012 miles per hour |
Factors on which rate of charging depends
Battery's current charge:- To protect and enhance battery life expectancy, charging slows significantly after 80 percent. The time it takes to 80 percent charge your battery might be the same as charging it the remaining 20 percent. This system prevents the battery from overcharging. Hence, enhances the battery's self-life.
Power Output:-The charger's power output significantly affects the charging rate. For 50 kW, only one hour of charging can add at least 278km of additional range. The type of vehicle can also dictate the time of charging.
Weather conditions:-Extreme cold temperatures can negatively impact your charging speed. The lithium-ion batteries used in electric automobiles are hyper-sensitive to cold temperatures.
Also Read: How long does it takes to charge an ev
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I charge my EV with DC?
Charging an electric automobile needs AC (Alternating Current) which is acquired via the grid and is then converted into DC form so it can be utilized by your vehicle.
2. Can I install DCfast charging station at home?
No, you can't install DC fast at your home, as houses and residential buildings work on the grid, and AC power is available only. Also, DC chargers are costly and cannot be afforded by everyone.
3. How much kW is a Level 3 DC charge?
The charging potential of the charger depends on its output power(kW). The higher the output, the quicker it can charge the vehicle. Also, kW out power varies with different factors such as location, model and brand.
4. Can I fast charge 100 per cent DC?
After rapidly charging the battery to 80 per cent, DC fast chargers usually slows down. If you fully charge using DC, then it will be slow as Level 2 AC chargers.
5. Why are DC motors not used in electric vehicles?
In particular, brushed DC motors cannot be used in EVs because of their limitations, such as low efficiency, large size, and high maintenance due to brush and collector structure.